Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) is an investment made by an entity or individual resident of one country into the business activity of a foreign country. FDI is considered a cross-border investment and a major source of non-debt financial resources for the economic development of a country. Foreign direct investment (FDI) plays an important role in transferring technology from a home country into a host country. It also promotes international trade through access to the foreign market.
A. Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) in India
India is one of the fastest-growing economies in the world. As per the data published by IMF (International Monetary Fund) India’s GDP is expected to grow 12.5% in FY 2021-22. The growing economy, infrastructure, manpower, incentives to foreign investors, growing demand, business opportunities, government policies are some of the reasons foreign nationals are attracted to and investing in India. As per the data released by the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), the total FDI equity inflows in India in FY 2020-21 is 59, 636 US$ million as compared to 40,001 US$ million in FY 2015-16.
A non-resident entity can invest in India, subject to the FDI Policy except in those sectors/activities which are prohibited. FDI in India has been continuously growing due availability of resources, infrastructure, business environment, and favorable policy of the Government of India. The foreign entity not only brings investment in India but also brings skills, knowledge, and technology with them.
B. Routes for Foreign Direct Investment in India
Investments by a foreign entity/individual in India can be done either through Automatic Route or Government Route.
- Automatic route: Under the Automatic route, no prior approval is required for making investments. Only information to the RBI within 30 days, of issue of equity instrument to Non Residents, is required
- Government route: Under the Government route, prior approval of the Government of India is required for making investments.
C. Sectors where Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) is Prohibited in India
As per FDI Policy, FDI in India is permitted in almost every sector. But still, there are some sectors where FDI is prohibited. Below mentioned are the sectors where FDI is not permitted in India.
- Lottery Business including Government/private lottery, online lotteries, etc.
- Gambling and Betting including casinos etc.
- Chit Funds.
- Nidhi Company.
- Trading in Transferable Development Rights (TDRs).
- Real Estate Business or Construction of Farm Houses
- Manufacturing of cigars, cheroots, cigarillos, and cigarettes, of tobacco or of tobacco substitutes.
- Activities/sectors not open to private sector investment (e.g. Atomic Energy and Railway Operations other than Railway Infrastructure)
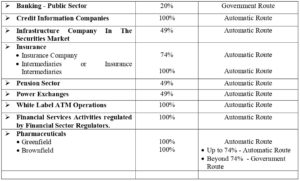
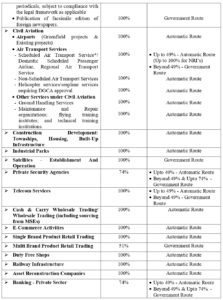
D. Sectors where Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) is Permitted in India
Below mentioned are the sectors/activities where FDI up to the limit as specified is permitted subject to applicable laws/regulations, security, and other condition as prescribed.
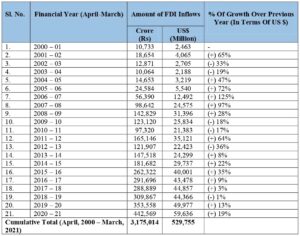
E. Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) in India
India has seen a tremendous increase in FDI inflows between Fy 2000-01 and Fy 2020-21. With the below table we can see the upward trend in FDI in India.
F. Conclusion
No doubt FDI has helped to boost the Indian economy. There are various reasons behind the increased FDI in India such as ease of doing business, investment facilitation, availability of resources, government reforms, etc. The Government of India has not only liberalized the FDI rules but also undertaken various initiatives to encourage and facilitate foreign investment in India. Now India has become a preferred investment destination among foreign investors.